You stare at your CRM and try to build next quarter’s sales forecast. Your pipeline looks healthy at first glance, but you’ve been burned before. Last quarter, you projected $500K in closed deals and came in at $340K. Your CFO questioned your budget. Your team missed quota. Now, according to recent Gartner research, 67% of sales operations leaders agree that creating accurate sales forecasts is more difficult today than it was three years ago. The stakes are higher and the margin for error is shrinking.
Here’s the reality: only 7% of sales organizations achieve forecast accuracy of 90% or higher. Yet sellers who leverage modern forecasting tools and AI are 3.7 times more likely to meet their sales quota. The difference between hitting your number and missing it often comes down to how you forecast. The process you follow. The methods you choose. The tools you use.
This definitive guide walks you through the complete sales forecasting process. You’ll learn a proven 6-step framework. You’ll explore 12 forecasting methods with real applications. You’ll discover the 13 best tools for 2026. You’ll understand how AI is transforming forecast accuracy. By the end, you’ll have everything you need to build a reliable forecast that drives smarter decisions and protects your revenue goals.
What Is a Sales Forecast?
A sales forecast is a data-backed prediction of the sales volume your business will generate over a specific period. Typically by month, quarter or year. It estimates how much revenue your team will close based on historical performance, current pipeline health, market conditions and the likelihood of individual deals converting.
Sales forecasts form the foundation for almost every other planning activity in your business. Your CFO uses them to manage cash flow and budget allocation. Your sales managers rely on them to set quotas and hire the right number of reps. Your marketing team adjusts campaigns based on whether forecasts show momentum or a slowdown. Without an accurate forecast, you’re flying blind. You make decisions on gut feel instead of data.
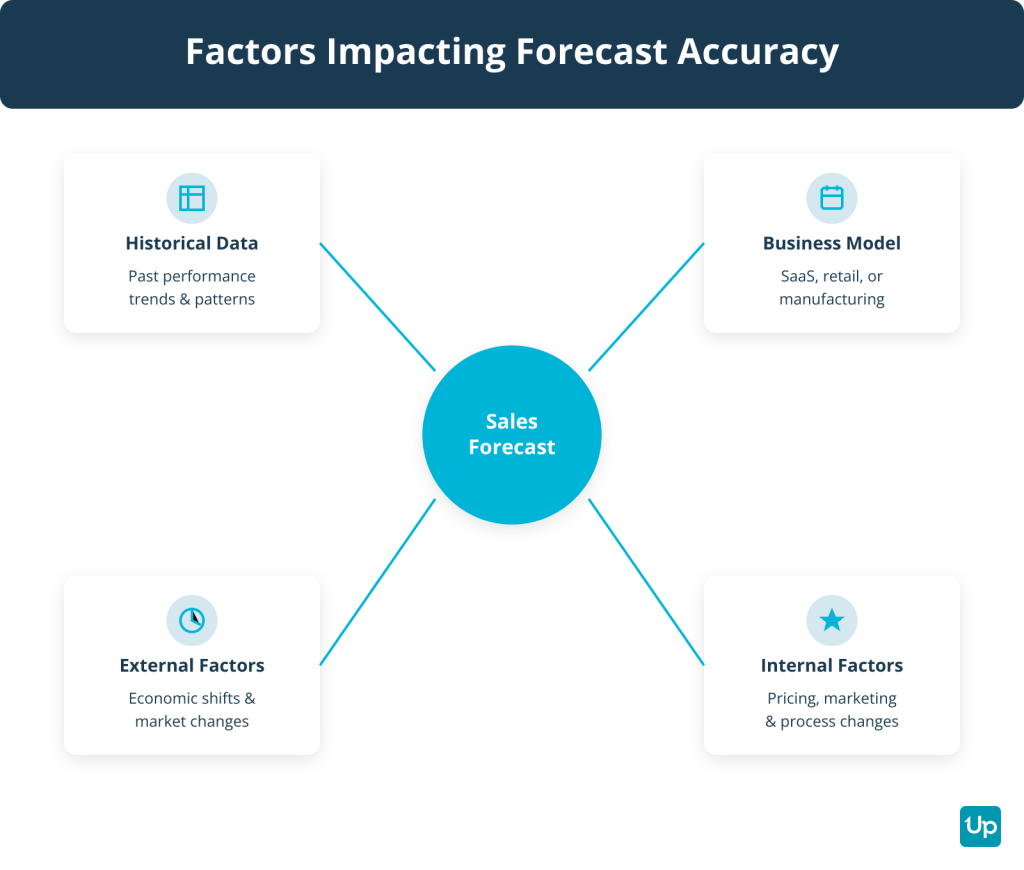
Several factors can impact the accuracy of your sales forecast. A lack of sales history makes it hard to identify trends, especially for startups or new product lines. The type of business you run matters too. SaaS companies face different dynamics than retail or manufacturing. External factors like economic downturns or regulatory changes can shift buyer behavior overnight. Internal factors such as pricing adjustments, new marketing initiatives or changes to your sales process can also throw off projections if not accounted for.
What Are the Different Types of Sales Forecasts?
The different types of sales forecasts include short-term, mid-term and long-term forecasts by time horizon, top-down and bottom-up forecasts by approach, and retail, services and SaaS forecasts by business model. Understanding these types helps you choose the right forecasting strategy for your situation.
By Time Horizon:
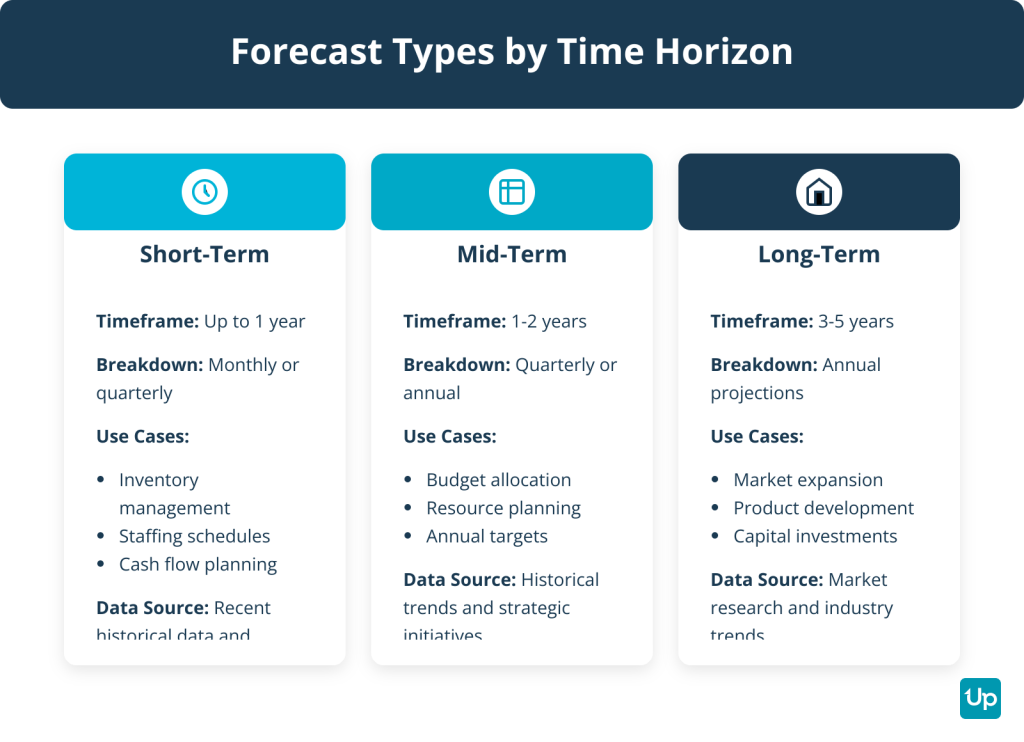
Short-term forecasting covers up to one year. You break it down by month or quarter. This type informs immediate operational decisions like inventory management, staffing schedules and short-term cash flow planning. It relies on recent historical data and your current sales pipeline.
Mid-term forecasting spans one to two years. It bridges the gap between day-to-day operations and long-term strategy. It helps with budget allocation, resource planning and setting annual revenue targets.
Long-term forecasting looks three to five years ahead. It supports strategic decisions like market expansion, new product development and major capital investments. These forecasts rely more on market research, economic indicators and industry trends than on your current pipeline.
By Approach:
Top-down forecasting starts with your total addressable market and estimates the market share you can capture. For example, if your TAM is $1 billion and you believe you can capture 5%, your forecast is $50 million. This approach is useful for setting strategic goals but can feel disconnected from operational reality.
Bottom-up forecasting starts at the granular level. Individual sales reps project their deals and you aggregate those projections upward. This approach is grounded in reality and leverages frontline insights, but it can sometimes be too conservative if reps sandbag their numbers.
By Business Model:
Retail forecasting focuses on predicting consumer demand to manage inventory levels. It uses historical sales data, seasonality patterns, promotional calendars and foot traffic trends.
Services forecasting for consulting firms or agencies is based on billable hours, project pipelines and contract renewals. The forecast tracks how many hours your team can sell and at what rate.
SaaS and consumption-based forecasting predicts how much existing customers will consume. API calls, data storage, active users. Rather than just tracking new subscriptions. This model is vital for revenue recognition and identifying upsell opportunities or churn risks early.
Why Is Sales Forecasting Crucial for Business Success?
Sales forecasting is crucial for business success because it powers almost every strategic and operational decision in your business. It enables accurate financial planning, effective sales activity planning, coordinated marketing efforts, controlled inventory levels and consistent pricing strategies.
Perform Accurate Financial Planning
Your CFO and finance team need to understand how much cash is coming into the business. A sales forecast gives them the visibility to calculate expected profit, manage cash flow and allocate capital wisely. Without it, you risk overspending on initiatives that won’t pay off or underfunding areas that could drive growth.
Plan Sales Activities
Sales forecasts help executives determine how many salespeople to hire, which quotas to assign and where to focus effort. When reps understand their targets and see how they tie to the forecast, they can prioritize the right deals and activities. This alignment helps your team hit their numbers consistently.
Coordinate Marketing
A sales forecast reveals whether your pipeline is healthy or shrinking. If the forecast shows a slowdown, marketing can ramp up campaigns to generate more leads. If a particular product line is underperforming, marketing can adjust messaging or shift budget to higher-performing offerings.
Control Inventory
For product-based businesses, a sales forecast helps you balance inventory levels. You can avoid overstocking, which ties up cash and increases storage costs, and prevent stockouts, which lead to lost sales. For SaaS companies, the same principle applies to customer support and success resources. You need the right capacity to serve your growing customer base.
Avoid Fluctuations in Pricing
An accurate sales forecast helps you maintain consistent pricing. A poor forecast can force you into panic mode. It leads to hasty discounts or price increases that confuse customers and erode profitability. When you forecast well, you can set pricing strategically and stick to it.
Recent research shows that 43% of sales leaders achieve forecast accuracy within 10%, but 79% of organizations still miss their forecast by more than 10%. The gap between good forecasting and poor forecasting is the difference between confident execution and reactive firefighting.

How Do You Create a Sales Forecast?
You create a sales forecast by defining your process and goals, gathering historical data, choosing your forecasting model, selecting your forecasting method, incorporating internal and external factors, and analyzing, reviewing and refining your forecast. Follow these six steps to build a forecast that is both accurate and actionable.
Step 1: Define Your Process and Goals
Start by establishing clear objectives for your forecast. Define the time period you’re forecasting. Monthly, quarterly or annually. Decide on the level of granularity you need. Will you forecast by product, by region, by sales team or by rep?
Align key stakeholders from sales, finance, marketing and supply chain on these goals. Make sure everyone agrees on what constitutes a “sale” in your business. Is it when the contract is signed, when the customer pays or when the service is delivered? Also, document your average sales cycle length, as this will inform your timeline assumptions.
Step 2: Gather Historical Data
Collect and review past sales data to identify trends, growth rates and seasonality patterns. Look back at least twice as far as the period you’re forecasting. If you’re forecasting six months ahead, analyze the past 12 months of data.
Break down this data by variables like product, price, sales rep and customer segment to form a “sales run rate.” Adjust for anomalies. One-time large purchases, black swan events like a pandemic or changes in your sales team or pricing structure. Clean data is the foundation of an accurate forecast.
Step 3: Choose Your Forecasting Model
Select the right forecasting model based on your data maturity and market stability. You have three main options:
Qualitative models rely on expert opinions and are useful when historical data is limited, such as for new products or startups. Time series models analyze historical data to find trends and seasonality. They work well for short-term forecasting in stable markets. Quantitative or causal models use statistical analysis to understand relationships between variables, which is ideal for complex scenarios with multiple influencing factors.
Step 4: Select Your Forecasting Method
Within your chosen model, select a specific method. Opportunity stage forecasting predicts revenue based on the probability of closing deals at each stage of your pipeline. Historical forecasting uses data from a previous identical period to project future sales. Lead-driven forecasting assigns values to leads based on their conversion likelihood. Multivariable analysis incorporates multiple internal and external factors for a more comprehensive view.
You don’t have to pick just one method. Many businesses blend multiple approaches to create a more balanced and resilient forecast.
Step 5: Incorporate Internal and External Factors
Adjust your forecast to account for factors that will influence future sales. Internal factors include planned marketing campaigns, product launches, pricing changes or shifts in your sales process. External factors include market trends, economic shifts, competitor activities and regulatory changes.
Involve cross-functional teams to gather these insights. Your marketing team knows what campaigns are launching. Your product team knows what features are coming. Your finance team tracks economic indicators. Bring these perspectives together to refine your forecast.
Step 6: Analyze, Review and Refine
Monitor your forecast accuracy against actual sales results. Set a regular cadence for forecast reviews. Weekly or monthly. Use these meetings to inspect deals, identify risks and coach reps.
Use dashboards and data visualization to analyze performance and identify variances. When you spot a gap between forecast and reality, dig into the root cause. Was it a change in buyer behavior? A longer sales cycle? A rep who sandbagged their numbers? This iterative process improves your model accuracy over time.

How Do You Choose the Right Sales Forecasting Method?
You choose the right sales forecasting method by matching it to your business model, data maturity, market stability and available resources. The forecast horizon, complexity of your business and access to modern tools all influence which method works best for your situation.
If you’re a startup with limited historical data, qualitative methods like intuitive forecasting or test market analysis are your best bet. These methods rely on expert judgment and real-world experiments rather than historical trends.
If you operate in a stable market with predictable sales cycles, historical forecasting or time series analysis will serve you well. These methods use past performance to project future results. They assume that patterns will continue.
If your business is complex with multiple products, regions and customer segments, multivariable analysis or causal models are the right choice. These methods incorporate a wide range of factors to create a more nuanced forecast.
If you have access to modern CRM tools and AI-powered platforms, AI-powered forecasting can improve accuracy. It analyzes vast datasets and identifies patterns humans might miss.
The key is to match the method to your situation. Don’t overcomplicate things if a simple approach will work. And don’t rely on a single method. Blend multiple techniques to create a more balanced forecast.
What Are the Most Common Sales Forecasting Methods?
The most common sales forecasting methods are opportunity stage forecasting, length of sales cycle forecasting, historical forecasting, lead-driven forecasting, test market analysis, multivariable and regression analysis, intuitive forecasting, time series analysis, pipeline forecasting, consumption-based forecasting, causal models and AI-powered forecasting. Each method has its strengths and is suited to different business contexts.
Opportunity Stage Forecasting
Opportunity stage forecasting calculates the likelihood of deals closing throughout your pipeline. Most businesses use a sales pipeline divided into stages. The probability of converting a prospect increases as they move deeper into the process.
To use this method, analyze your team’s current performance to assign a probability to each stage. For example, a sales-accepted lead might have a 10% probability of closing, a sales-qualified lead 25%, a proposal sent 40%, negotiating 60% and a contract sent 90%.
Take each deal’s potential value and multiply it by the win likelihood. Sum these weighted values across all deals in your pipeline to get your forecast.
This method is great if you have historical data, lots of leads in your pipeline and you need a quick estimate. However, it’s not the most accurate option because many random factors affect those probabilities.
Length of Sales Cycle Forecasting
Length of sales cycle forecasting finds the average length of your sales cycle and uses that to predict when deals will close. This method helps you identify opportunities to expedite the sales process.
Calculate your average sales cycle length using this formula: total number of days to close all deals divided by the number of closed deals. For instance, if you closed four deals in 28, 15, 50 and 38 days respectively, your average sales cycle is 33 days.
With this information, you can look at your pipeline and estimate how likely you are to close deals based on how old they are. The closer a deal moves toward the average sales cycle length, the more likely it will close.
This method is ideal for sales managers who want to learn more about the deals in their pipeline and differentiate between different types of leads. You might find, for example, that web leads close faster than email leads.
Historical Forecasting
Historical forecasting is a quick and simple technique. You look back at your previous performance within a certain timeframe and assume your future performance will be equal or superior.
This method helps you understand seasonality and outside factors that affect your sales. You might find, for instance, that the holidays are a slow time for your business. Historical data helps you prepare.
However, historical forecasting assumes that buyer demand will remain constant, which is no longer a given. This could lead you to overestimate your sales and create an inaccurate forecast.
This method is ideal for businesses that need a quick and easy way to project sales over a given period. That said, historical data should be used as a benchmark rather than the sole foundation of a sales forecast.
Lead-Driven Forecasting
Lead-driven forecasting involves reviewing each lead in your pipeline and determining how likely the deal will close. That likelihood is determined by exploring factors like the value of the opportunity, the performance of your salespeople, seasonality and more.
This method is time-consuming and makes sense for businesses with fewer high-value leads. It wouldn’t be efficient for a SaaS business that operates on volume.
The big benefit of this method is its accuracy. If you have reliable and rigid data to base your analysis on, this method can give you a deeper insight into each lead.
This method is appropriate for businesses with a lower number of leads. Inside salespeople, for instance, will want a clearer picture of every lead in their pipeline.
Test Market Analysis
Test market analysis is the process of developing a product or service and introducing it to a test market to forecast sales and get an approximation of future sales.
This limited rollout allows businesses to track the performance of the new offering and monitor things like consumer awareness, repeat purchase patterns and more. This is a data-gathering exercise. It feeds businesses with the information they need to create accurate sales forecasts.
This approach is perfect for businesses that need to perform real-world experiments to gather useful information. A new business can use this method to collect sales data and predict where future sales can come from. The limited rollout is also useful from a product perspective, as adjustments can be made based on feedback.
A big issue with this form of forecasting is that one test market may not be like the others. Your data might not reflect the wider reality, so you must make prudent choices that provide accurate information.
Multivariable and Regression Analysis
Multivariable analysis is a statistical method that analyzes the relationship between multiple variables to forecast outcomes. Regression analysis is a specific type of multivariable analysis that models the relationship between a dependent variable, such as sales revenue, and one or more independent variables, such as factors that influence the outcome.
Unlike time-series models that rely solely on past data of the variable itself, causal models incorporate external and internal factors that influence the outcome. The goal is to create a mathematical formula, often through regression analysis, that quantifies how changes in these predictors impact the forecast variable.
Multiple linear regression is common in sales forecasting. Independent variables might include advertising spend, number of sales calls, website traffic, seasonal trends, pricing strategies, competitor pricing, customer demographics and economic indicators like interest rates.
The output shows how much sales are expected to change for each one-unit increase in an independent variable. This assumes other factors remain constant.
This method brings together factors like the average length of your sales cycle, the performance of your salespeople and historical forecasting. The success of this method hinges on the accuracy of your salespeople and their reporting, as well as the quality of the forecasting tools you use.
Multivariable forecasting is most appropriate for larger and well-organized businesses, as it requires the data and tools necessary to blend various forecasting methods into one. This could be the right choice if you need the most accurate forecast method possible.
Intuitive Forecasting
Your salespeople are on the front lines. Their experience is valuable. They often have a good idea of how likely they are to close a particular deal and can use educated guesses to assess the situation.
Experienced salespeople can take emotion out of the equation and rely on their experience and knowledge to make accurate predictions. Some businesses decide to incorporate those gut instincts into the way they forecast a particular sale.
Some businesses will add a score to the conversion probability of their various prospects according to the gut feeling of their salespeople.
This method is useful for businesses that lack historical data. Without the quantifiable data to provide the basis for your sales forecasting, you might have to turn to more qualitative assessments from your salespeople.
The downside of this method is clear. These assessments are subjective. You might find that your salespeople are often more optimistic in their projections. Those projections should be taken with a pinch of salt, but they are better than nothing.
Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis is a quantitative sales forecasting method that uses historical data collected over specific time intervals to predict future sales. This statistical technique identifies and analyzes underlying patterns. Trend, seasonality, cyclical patterns and irregular noise.
Trend refers to the long-term movement of sales data. Seasonality captures predictable recurring fluctuations, such as holiday shopping spikes. Cyclical patterns are longer-term waves that might correlate with economic cycles. Irregular noise represents random variations.
By decomposing past sales data into these components, the model can project them forward to create a forecast.
This method is best suited for stable businesses with significant historical sales data. Typically at least two to three years. And predictable sales cycles. It is less effective for new businesses or volatile markets.
Pipeline Forecasting
Pipeline forecasting estimates future revenue by analyzing all active deals currently in the sales pipeline. You assign a probability of closing to each deal based on its current stage in the sales cycle.
The total forecast is the sum of each deal’s value multiplied by its stage-based probability. This provides a real-time, data-driven forecast based on current sales activities.
This method differs from opportunity stage forecasting, which is a more specific application focusing on distinct stages with historical win rates for each specific stage. Pipeline forecasting provides a broader, more dynamic view of your entire pipeline at any given moment.
Consumption-Based Forecasting
Consumption-based forecasting is a method used to predict future revenue and resource needs for businesses with usage-based or pay-as-you-go pricing models. Unlike traditional subscription forecasting, which relies on fixed recurring revenue, this model predicts how much of a service or product customers will consume over a period.
It is essential for SaaS, IaaS and other digital service companies where revenue is tied to customer usage. According to a 2022 report by OpenView Partners, companies with usage-based pricing grow faster. 29% year-over-year growth versus 22% for others. But they face greater forecasting challenges. Another report indicates that 60% of B2B SaaS companies have implemented or are testing a consumption model.
The process involves analyzing historical usage data to identify patterns, seasonality and customer behavior trends. Key inputs include historical usage patterns at customer and cohort levels, seasonal variations, customer growth rates and specific usage metrics like API calls, data storage or compute hours.
Primary benefits include more accurate revenue projections, better capacity and resource planning, optimization of pricing strategies and early identification of customer churn risks or upsell opportunities.
Causal Models
Causal models, also known as associative or econometric models, are a quantitative forecasting technique that predicts future outcomes by identifying and analyzing the cause-and-effect relationships between independent variables, which are predictors, and a dependent variable, which is the value being forecasted.
Unlike time-series models that rely solely on past data of the variable itself, causal models incorporate external and internal factors that influence the outcome. The goal is to create a mathematical formula, often through regression analysis, that quantifies how changes in these predictors impact the forecast variable.
Common independent variables in sales forecasting include marketing spend, promotional activities, competitor pricing, economic indicators, seasonality and weather patterns.
The main advantage is explanatory power. It helps businesses understand why sales are changing, not just that they are changing. This allows for robust scenario planning. However, these models are more complex and data-intensive to build and maintain compared to simpler forecasting methods.
AI-Powered Forecasting
AI-powered forecasting uses machine learning algorithms and predictive analytics to analyze vast and diverse datasets to predict future sales. Unlike traditional methods that rely on historical sales data and manual analysis, AI forecasting incorporates structured data like CRM data and sales rep activity, as well as unstructured data such as customer emails, call recordings, social media sentiment and broader market trends.
The core of this method is its ability to identify complex patterns, correlations and anomalies invisible to human analysis. Machine learning models learn from new data. This allows forecasts to adapt to changing market conditions.
This results in higher forecast accuracy. Studies suggest improvements of 10-20%. Key benefits include reduction in human bias, automation of manual tasks and real-time insights into pipeline health and deal-level probabilities.
What Are the Best Sales Forecasting Software and Tools for 2026?
The best sales forecasting software and tools for 2026 are Pipedrive, Salesforce, HubSpot, Clari, Gong.io, Aviso, Anaplan, Zoho CRM, Outreach, Forecastio, BoostUp.ai, Workday Adaptive Planning and SPOTIO. The right tools can improve your forecasting accuracy and save your team hours of manual work.
Pipedrive
Pipedrive offers intuitive sales forecasting through its visual pipeline management, which allows users to track deal progress and potential revenue in real-time. This is enhanced by an AI Sales Assistant that predicts deal win probability and provides data-driven suggestions to improve forecast accuracy.
Salesforce
Salesforce Sales Cloud offers robust, customizable forecasting with real-time rollups, AI-powered predictions via Einstein and flexible forecast types for complex enterprise needs. Its forecasting tools are available in Professional, Enterprise and Unlimited editions with features including customizable forecast categories and the ability to create custom forecast types based on different data models.
HubSpot
HubSpot’s forecasting tool, part of Sales Hub, offers user-friendly, CRM-integrated forecasting with customizable categories, goal tracking and AI-powered deal insights to help SMBs easily predict revenue. The tool is designed for ease of use. It pulls data from the CRM to eliminate manual spreadsheet work.
Clari
Clari is a leading Revenue Orchestration Platform that uses AI to unify data and improve forecasting accuracy. It provides a comprehensive view of the pipeline by capturing and analyzing all revenue-critical signals. This enables teams to forecast with over 95% accuracy and manage deals more effectively.
Gong.io
Gong.io is a Revenue Intelligence platform that uses conversational intelligence to analyze customer interactions. By using AI to analyze calls, emails and meetings, it identifies risks and provides data-backed insights that help create more accurate sales forecasts.
Aviso
Aviso is a US-based revenue intelligence platform that uses AI to provide predictive forecasting and deal guidance for go-to-market teams. The platform uses a proprietary time-series AI engine and machine learning to unify CRM data and provide predictive forecasting. It claims up to 98% forecast accuracy.
Anaplan
Anaplan is a connected planning platform ideal for complex, enterprise-level sales forecasting that unifies data across finance, sales and operations for real-time scenario modeling. It excels at connecting financial, sales and operational plans into a single, unified system. This eliminates reliance on siloed spreadsheets.
Zoho CRM
Zoho CRM offers strong value for SMBs with affordable, scalable plans and integrated sales forecasting features to predict revenue and track deal pipelines. Its forecasting tools are available from the Professional plan and allow teams to estimate future sales based on revenue or deal quantity.
Outreach
Outreach embeds AI-powered forecasting into its sales engagement platform. It uses real-time deal insights and buyer activity to improve forecast accuracy and predictability. It connects forecasting to sales engagement activities by analyzing real-time buyer signals and deal health.
Forecastio
An AI-powered sales forecasting platform built natively for HubSpot. It is designed to automate revenue projections and provide performance insights with up to 95% accuracy.
BoostUp.ai
An AI-powered revenue intelligence platform that unifies sales activity and conversation data to deliver accurate forecasting, deal risk analysis and rep coaching.
Workday Adaptive Planning
A cloud-based enterprise performance management solution for company-wide planning. This includes sales. It enables sales organizations to model and plan territories, quotas and capacity to align resources with revenue targets and improve forecast predictability.
SPOTIO
A field sales engagement platform that provides tools for outside sales teams to improve forecasting predictability. It offers real-time sales activity and pipeline tracking, territory management and performance analytics to give leaders a data-driven view of what’s happening in the field.
What Is the Role of AI in Sales Forecasting?
AI plays a transformative role in sales forecasting by automating data collection, identifying complex patterns, reducing human bias and improving accuracy by 10-20%. Traditional methods suffer from low accuracy. Only 7% of sales organizations achieve 90% or higher forecast accuracy according to Gartner.
AI addresses these challenges by processing vast amounts of structured and unstructured data from CRMs, emails, calendars and external sources like market trends and economic indicators. Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to identify factors that correlate with sales outcomes. This creates predictive models that are more accurate and dynamic than human-led efforts.
Key benefits include enhanced accuracy. AI improves forecast accuracy by 10-20% according to McKinsey. Some companies like Danone achieved 20% improvement and reduced lost sales by 30%. AI models are data-driven. This mitigates human bias and provides objectivity.
Efficiency and automation are major advantages. Cisco reduced forecasting time by 30% using AI. AI also uncovers hidden patterns and provides real-time insights into pipeline health.
By 2025, Gartner predicted that 75% of B2B sales organizations would use AI-guided selling solutions. The AI for Sales and Marketing Market is valued at USD 57.99 billion in 2025 and projected to grow to USD 240.58 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 32.9%.
Future trends include ‘Agentic AI’ for autonomous task handling and Generative AI integration for actionable selling advice.

Practical Sales Forecasting Examples and Templates
Here are practical examples and templates to help you build your own sales forecast.
Example of a Startup Sales Forecast
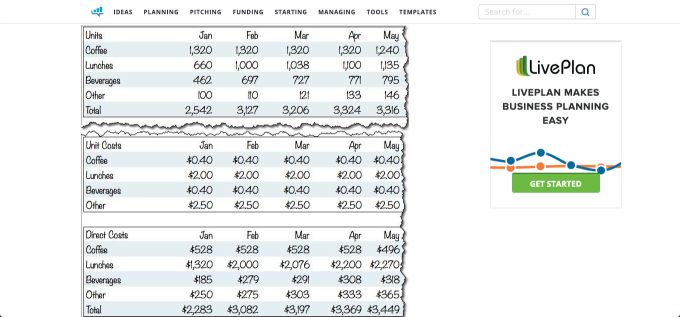
This example from Tim Berry, chairman and founder of Palo Alto Software, looks at what a startup sales forecast might look like. Tim sets the scene and describes Magda’s situation. She wants to open a small café in an office park.
He goes on to show how Magda would establish a base case, estimate her monthly capacity and what type of sales she could expect. To wrap up, she goes through her month-by-month estimates for her first year and estimates her direct cost.
This is a great exercise and unmissable reading for new entrepreneurs dreaming up a new venture. A startup sales forecast example involves using inputs like Marketing Budget, Cost per Click, Paid and Organic Traffic and Conversion Rate to calculate total sales across multiple years.
Example of a B2B Sales Forecast
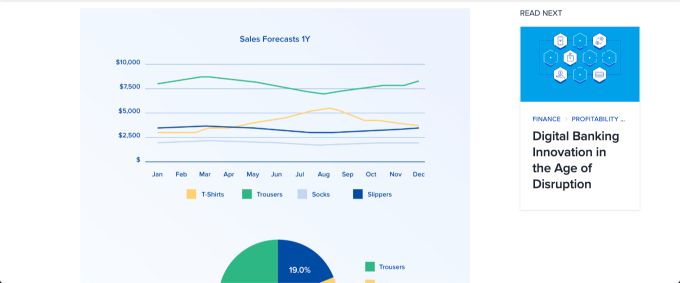
This simple sales forecasting guide from Toptal Research also includes a simple example that forms the basis of the guide. These simple visuals and data will give you a good idea of how you can put your sales forecasting efforts together and what it will look like.
This example also shows that you can forecast sales in an attractive way and inform the sales teams. Sales forecasting doesn’t have to be boring columns of data. You can bring your sales forecast to life with colorful visuals.
For a B2B sales forecast, an example would be a pipeline-based forecast that assesses each deal’s value and the probability of closing based on its stage in the sales funnel. For instance, a B2B SaaS company might analyze a 15% annual growth in renewals and combine this with a pipeline analysis that considers deal size, closing probability by stage and historical rep close rates.
Template for Monthly Sales Forecasting (Excel/Sheets)
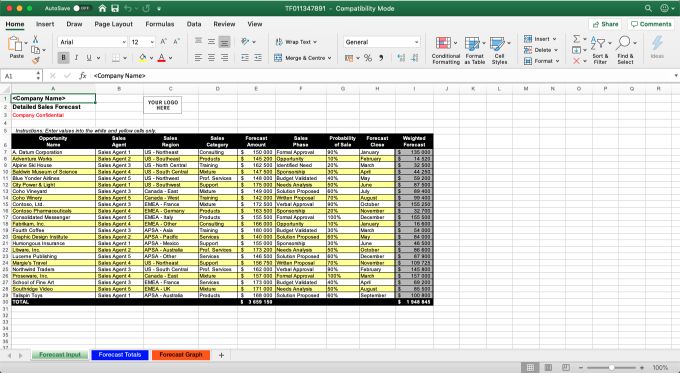
This detailed sales forecast template from Microsoft makes it simple for you to estimate your monthly sales projections. The formula comes with pre-built formulas and worksheet features that result in an attractive and clear template. The template also relies on a weighted sales forecasting method based on the probability of closing each opportunity.
Even if you do not use this exact template, it’s a great file to use. It can give you a great idea of the information you need to include and how it might come together in a spreadsheet format.
Template for Annual Sales Forecasting (Excel)
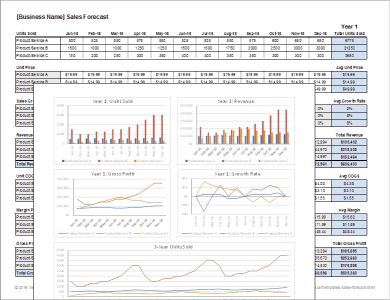
This free sales forecast template helps you keep a handle on key information like unit sales, growth rate, profit margins and gross profit. The template is already set up to help you compare and analyze a range of products and services on a monthly basis. The chart also includes a range of sample charts that can be used to communicate the contents of your sales forecast in an effective and accurate way.
The same worksheet can be used to create monthly and yearly forecasts. You can play with the template to find your desired view and information.
Template for SaaS Sales Forecasting
This simple forecasting template helps you to put together an effective sales forecast. This finished product can then be used to grow your revenues and hit your quotas.
This template is effective for small businesses and startups that need to project sales and prioritize deals at the early stages of their business. Freshworks also explains that the template can help businesses achieve a higher rate of on-time delivery and accurate hiring projections.
The free sales forecast template is intuitive to use. Again, it’s great to flick through the spreadsheet to understand what you need in a sales forecast and how it can be put together.
Template for Small Business Sales Forecasting
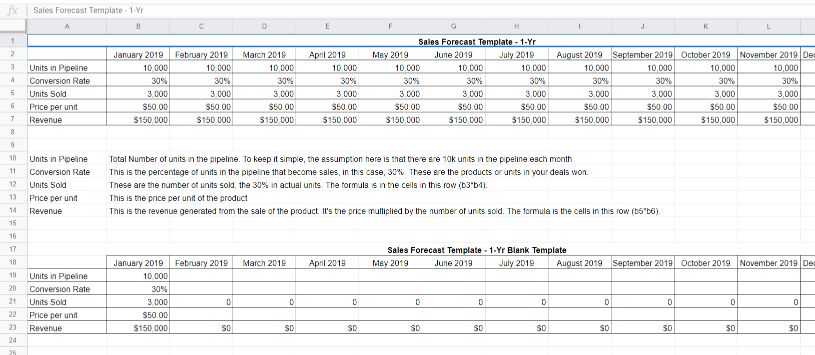
This sales forecast template is perfect if your CRM doesn’t currently offer built-in sales forecasting. This template can help you create a forecast from scratch that is adjusted to your own particular needs much quicker.
The template is available in various formats. PDF, Excel and Google Sheets. This is great news if you create your small business on your own terms and have limited software access.
Again, this template is clear and simple to use. All of the fields are explained within the spreadsheet. You don’t have to worry about going elsewhere to find definitions.
Free, downloadable sales forecast templates for Excel and Google Sheets are available from Smartsheet. This includes templates for various use cases like a 12-month forecast, monthly forecast and a specific ‘Startup Sales Forecast Template’.
What Are the Best Practices for Accurate Sales Forecasting?
The best practices for accurate sales forecasting are establishing a standardized sales process, maintaining high-quality data, choosing the right forecasting methods, involving and training your sales team, conducting regular forecast reviews, leveraging modern forecasting tools, analyzing historical performance and accounting for external and internal factors. Follow these practices to improve the accuracy of your sales forecast.
1. Establish a Standardized Sales Process
Define clear, objective criteria for each stage of the sales cycle. This ensures every team member qualifies and moves opportunities consistently. It reduces subjectivity and cleans up pipeline data.
2. Maintain High-Quality Data
A forecast is only as good as its data. Clean your CRM data to remove duplicates, fill in missing information and correct errors. Ensure all customer interactions and deal updates are logged in a timely manner.
3. Choose the Right Forecasting Method(s)
Don’t rely on a single technique. Blend different methods. Historical, opportunity stage and AI-powered forecasting. This creates a more balanced and resilient prediction. The right mix depends on your business model, data maturity and market stability.
4. Involve and Train Your Sales Team
Forecasting shouldn’t be a top-down mandate. Train reps on the importance of accuracy and how to forecast properly. Involve them in the process. This leverages their on-the-ground insights and fosters accountability.
5. Conduct Regular Forecast Reviews
Implement a consistent cadence for forecast reviews. Weekly or bi-weekly. Use these meetings to inspect deals, identify risks and coach reps, rather than just for reporting numbers.
6. Leverage Modern Forecasting Tools
Move beyond spreadsheets. Use CRM systems and specialized AI-powered forecasting tools to automate data collection, analyze trends and reduce manual effort. This leads to more accurate, real-time insights.
7. Analyze Historical Performance and Track Accuracy
Maintain an archive of past forecasts to compare against actual results. This helps you identify patterns in forecast errors, understand biases and refine your process over time.
8. Account for External and Internal Factors
A forecast shouldn’t exist in a vacuum. Consider the impact of market trends, seasonality, economic shifts, competitor activities and internal changes like new marketing campaigns or product launches.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the difference between a sales forecast and a revenue forecast?
A sales forecast focuses on ‘bookings,’ which is the total value of new contracts signed within a specific period. It represents sales momentum and future growth potential. A revenue forecast deals with ‘recognized revenue,’ which is the portion of contract value earned and recorded on financial statements as service is delivered. This adheres to accounting principles like GAAP.
For subscription models, this distinction is crucial. For example, if a customer signs a $12,000 annual contract in January, the sales forecast shows a $12,000 booking for that month. However, the revenue forecast will show only $1,000 of recognized revenue each month for the entire year, as the service is provided over time.
Bookings represent the customer’s commitment. Recognized revenue reflects actual income earned during a period. Therefore, a sales forecast indicates potential revenue, whereas a revenue forecast provides a more accurate picture of the company’s actual financial performance for a given period.
How far ahead should I forecast sales?
The forecast horizon depends on your business model and planning needs. Short-term forecasts cover up to one year and are most accurate for operational planning. Mid-term forecasts span one to two years and help with budget allocation. Long-term forecasts look three to five years ahead and support strategic decisions like market expansion.
What is a good sales forecast accuracy rate?
A good sales forecast accuracy rate is within 10% of actual results. However, only 7% of sales organizations achieve 90% or higher forecast accuracy according to Gartner. Most organizations should aim for accuracy within 10-15% and work to improve that number through better data, processes and tools.
Can I use multiple forecasting methods at once?
Yes, and you should. Blend multiple forecasting methods. Historical, opportunity stage and AI-powered forecasting. This creates a more balanced and resilient prediction. This approach helps you compensate for the weaknesses of any single method.
How do I improve my sales forecast accuracy?
Improve your sales forecast accuracy by establishing a standardized sales process, maintaining high-quality CRM data, choosing the right forecasting methods, involving and training your sales team, conducting regular forecast reviews, leveraging modern forecasting tools, analyzing historical performance and accounting for external and internal factors.
Conclusion
Sales forecasting is the foundation of smart business planning. It powers financial decisions, guides sales activities, aligns marketing efforts and protects you from costly surprises. The difference between an accurate forecast and an inaccurate one is the difference between hitting your goals and scrambling to explain why you missed them.
This guide gave you a proven 6-step process, 12 forecasting methods, 13 modern tools and 8 best practices to build a forecast you can trust. Now it’s time to put it into action. Start by defining your goals, gathering your data and choosing the right method for your business. Leverage modern tools like AI-powered forecasting platforms to automate the heavy lifting and improve accuracy.
But remember, even the best forecast is only as good as the leads in your pipeline. You need a steady flow of qualified prospects to make those projections a reality. Learn more about UpLead today and discover how our platform can help you find, connect and engage with the right prospects to hit your forecast every single time.